IP Packet Filter Configurator - END-OF-LIFE
After careful consideration I have decided to end-of-life this tool. Although it may still have *some* relevance on very old Windows systems, that residual utility does not outweigh the support costs. :| So, as of today this tool will have a page but no longer be available for download.
I hope that this does not cause anyone significant inconvenience.
Regards - Eric
Current version: 1.0
Although everyone needs a firewall or router, not everybody always has access to one. Windows XP provides a firewall as part of the OS. Windows 2000 and lower OS versions do not. However, Windows 2000 and XP both provide IP packet filtering. Unfortunately, the process of configuring the filter is tedious, and must be performed for every adapter (network card) individually. If you want to disable and/or enable groups of ports life gets frustrating quickly. For example, disabling filtering wipes out the list of ports that you just painstakingly typed in, one at a time!
This tool is intended to remove some of that tedium by providing direct access to the configuration parameters (values in the registry) for UDP and TCP packet filtering. The tool works with an XML file that specifies groups of ports required for various applications (OS services, games, etc.). You can modify the XML file to include your favorite groups and select that configuration with a single click! You can select groups of applications as well as specify ports manually, and you can apply these configurations to each adapter in turn. No more manual tedium!
The entries in the XML file look like:
-
<application name="Diablo" udp="6112-6119" tcp="6112-6119" vendor="Blizzard Entertainment" note="Allow port 6112-6119 TCP and UDP out and in; www.blizzard.com" />
Each TCP and UDP port list contains comma-separated ranges and values.
NOTE 1: This tool uses the MSXML parser to read the XML configuration file. If you get errors on startup related to XML you will need to obtain the appropriate MSXML DLL (msxml2.dll, msxml3.dll, or msxml4.dll).
NOTE 2: There are reasons why you want to use a firewall, but ip packet filtering can be quite useful. It is important to remember:
- "IP Filtering can filter only inbound traffic. This feature does not affect outbound traffic or TCP response ports that are created to accept responses from outbound requests. Use a firewall, IPSec Policies or Routing and Remote Access packet filtering if you require more control over outbound access."
Files: THIS TOOL IS END-OF-LIFE --REF
Screen Shots
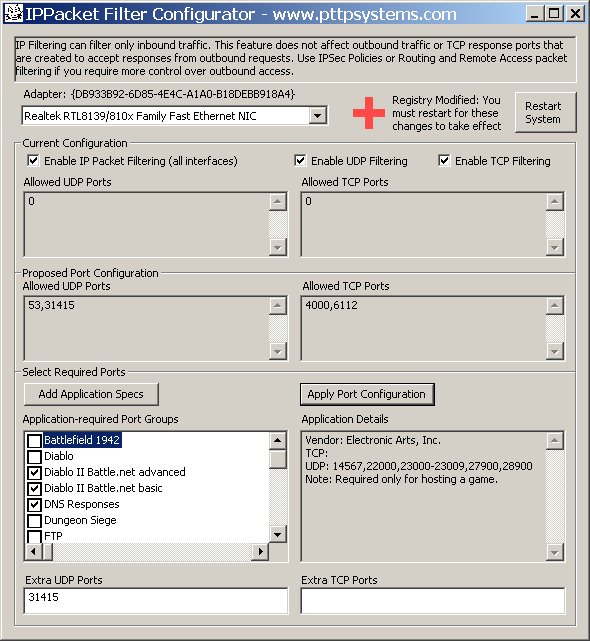
Want to know why the manual process is frustrating? Here is text straight off of Microsoft's site.
Microsoft's Directions
To configure TCP/IP Filtering, follow these steps.
Note To perform this procedure, you must be a member of the Administrators group or the Network Configuration Operators group on the local computer.
- Click Start, point to Control Panel, right-click Network Connections, and then click Open.
- Right-click the network connection where you want to configure inbound access control, and then click Properties.
- Under AdapterName Connection Properties on the General tab, click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
- In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click Advanced.
- Click the Options tab.
- Click TCP/IP Filtering, and then click Properties.
- Click to select the Enable TCP/IP Filtering (All adapters) check box.
Note When you select this check box, you enable filtering for all adapters. However, filter configuration must be done on each adapter. When TCP/IP Filtering is enabled, you can configure each adapter by selecting the Permit All option, or you can allow only specific IP protocols, TCP ports, and UDP ports to accept inbound connections. For example, if you enable TCP/IP Filtering and you configure the external network adapter to permit only port 80, this allows the external network adapter to accept Web traffic only. If the internal network adapter also has TCP/IP Filtering enabled but is configured with the Permit All option selected, this allows for unrestricted communication on the internal network adapter. - Under TCP/IP Filtering, there are three columns with the following labels:
- TCP Ports
- UDP Ports
- IP Protocols
- Permit All. Select this option if you want to permit all packets for TCP or UDP traffic.
- Permit Only. Select this option if you want to permit only selected TCP or UDP traffic. Click Add, and then type the appropriate port or protocol number in the Add Filter dialog box. You cannot block UDP or TCP traffic by selecting Permit Only in the IP Protocols column and by then adding IP protocols 6 and 17.
TCP/IP Filtering can filter only inbound traffic. This feature does not affect outbound traffic or TCP response ports that are created to accept responses from outbound requests. Use IPSec Policies or Routing and Remote Access packet filtering if you require more control over outbound access.
Note If you select Permit Only in UDP Ports, TCP Ports, or the IP Protocols column and the lists are left blank, the network adapter will not be able to communicate with anything over a network, either locally or to the Internet.
